Understanding Motherboard Form Factors
ATX – Features and Typical Use Cases
Motherboard sizes can seem like a confusing maze, but understanding their distinctive features is essential for optimizing your PC build. The ATX form factor, for example, remains the industry standard, renowned for its balance of expandability and versatility. With its dimensions typically measuring 12 x 9.6 inches, ATX motherboards provide ample room for multiple PCIe slots, RAM slots, and storage connectors. This makes them ideal for gaming rigs, workstations, or any setup where future upgrades are a priority.
In terms of typical use cases, ATX motherboards are perfect for users who want a robust foundation for high-performance components. They often support advanced features like multiple graphics cards and extensive cooling options, catering to enthusiasts and professionals alike. For those seeking a more compact solution without sacrificing power, the ATX form factor offers a compelling combination of size and capability, making it a go-to choice in the realm of motherboard sizes.
Micro-ATX – Compact Alternative for Smaller Builds
Motherboard sizes are not merely dimensions—they are the very foundation of a computer’s soul, shaping its capacity for expansion and innovation. Among these, Micro-ATX stands out as a compact alternative that balances power with space efficiency. For those who crave a smaller footprint without sacrificing performance, this form factor offers a compelling solution. Its dimensions, typically measuring 9.6 x 9.6 inches, make it ideal for smaller cases while still supporting essential components.
In the realm of motherboard sizes, Micro-ATX delivers a surprising versatility. It often includes multiple PCIe slots and sufficient RAM slots, making it suitable for mid-range builds or office setups. For users who desire a leaner, more streamlined machine, this form factor is a testament to ingenuity—providing just enough room for high-performance components to thrive, all within a compact chassis.
Mini-ITX – Optimal for Small Form Factor PCs
Motherboard sizes can dramatically influence the architecture of a compact yet potent system. Among the various options, Mini-ITX stands out as the ideal choice for those seeking to craft small form factor PCs without compromising on performance. With dimensions typically measuring just 6.7 x 6.7 inches, Mini-ITX motherboards are the epitome of space efficiency, fitting neatly into even the most constrained cases. This size isn’t just about saving room; it’s about unlocking a new realm of possibilities for innovative designs.
What makes Mini-ITX truly captivating is its ability to house essential components while maintaining a minimalist footprint. Despite its diminutive stature, it supports high-performance CPUs, multiple RAM slots, and even dedicated graphics cards—if the chassis allows. For enthusiasts and professionals alike, understanding motherboard sizes like Mini-ITX is crucial for tailoring a system that balances power and portability flawlessly.
Extended ATX (E-ATX) – High-Performance and Gaming Systems
In the realm of high-performance and gaming systems, the choice of motherboard sizes becomes a defining factor in the architecture of the ultimate powerhouse. Extended ATX (E-ATX) motherboards are the titans of the motherboard sizes spectrum, designed to conquer the demands of enthusiasts who crave expansive capabilities. With dimensions often stretching beyond the standard, these motherboards offer ample room for multiple graphics cards, extensive RAM configurations, and sophisticated cooling solutions—transforming a mere PC into a veritable fortress of power.
What sets E-ATX apart is not just its size but its capacity to support a symphony of components, each playing a crucial role in performance. For those seeking to push boundaries, the large footprint of motherboard sizes like E-ATX allows for innovative layouts and superior expandability. Whether for ultra-high-end gaming rigs or professional workstations, understanding the nuances of motherboard sizes is essential. It’s not just about fitting components; it’s about sculpting a system that embodies both grandeur and precision—an engineering marvel in every sense.
Other Form Factors – Mini-DTX, FlexATX, and More
Motherboard sizes are more than mere dimensions; they are the canvas upon which the architecture of a computer is painted, each size whispering its own story of potential and purpose. While ATX remains the most familiar, the world of motherboard sizes is a labyrinth of possibilities, where each form factor unlocks a different realm of customization and performance. Among these, miniaturized variants like Mini-DTX and FlexATX carve out niches for space-conscious builders without sacrificing essential features.
Understanding motherboard sizes involves appreciating their unique footprints and the roles they play in system design. For example, Mini-DTX motherboards are tiny marvels, perfect for ultra-compact setups, yet they still manage to support a surprising array of components. Similarly, FlexATX offers flexibility—literally—allowing for versatile placements within constrained cases. These smaller form factors often adopt a minimalist aesthetic but are packed with ingenuity, making them ideal for discreet yet powerful systems.
- Mini-DTX: The epitome of space efficiency, ideal for HTPCs and compact desktops.
- FlexATX: Versatile, adaptable, perfect for custom builds where size and function must harmonize.
- Other niche sizes: These include proprietary or specialized formats designed for specific applications, each adding depth to the diverse universe of motherboard sizes.
Each of these variations expands the horizon for enthusiasts and professionals alike, emphasizing that motherboard sizes are not just about fitting components—they are about sculpting a symphony of technology within the constraints of space, performance, and aesthetics. In this enchanted landscape of motherboard sizes, every form factor is a chapter in the ongoing story of innovation and ingenuity, inviting builders to dream beyond the ordinary.
Size Comparisons and Dimensions
Standard Dimensions – ATX and Micro-ATX Measurements
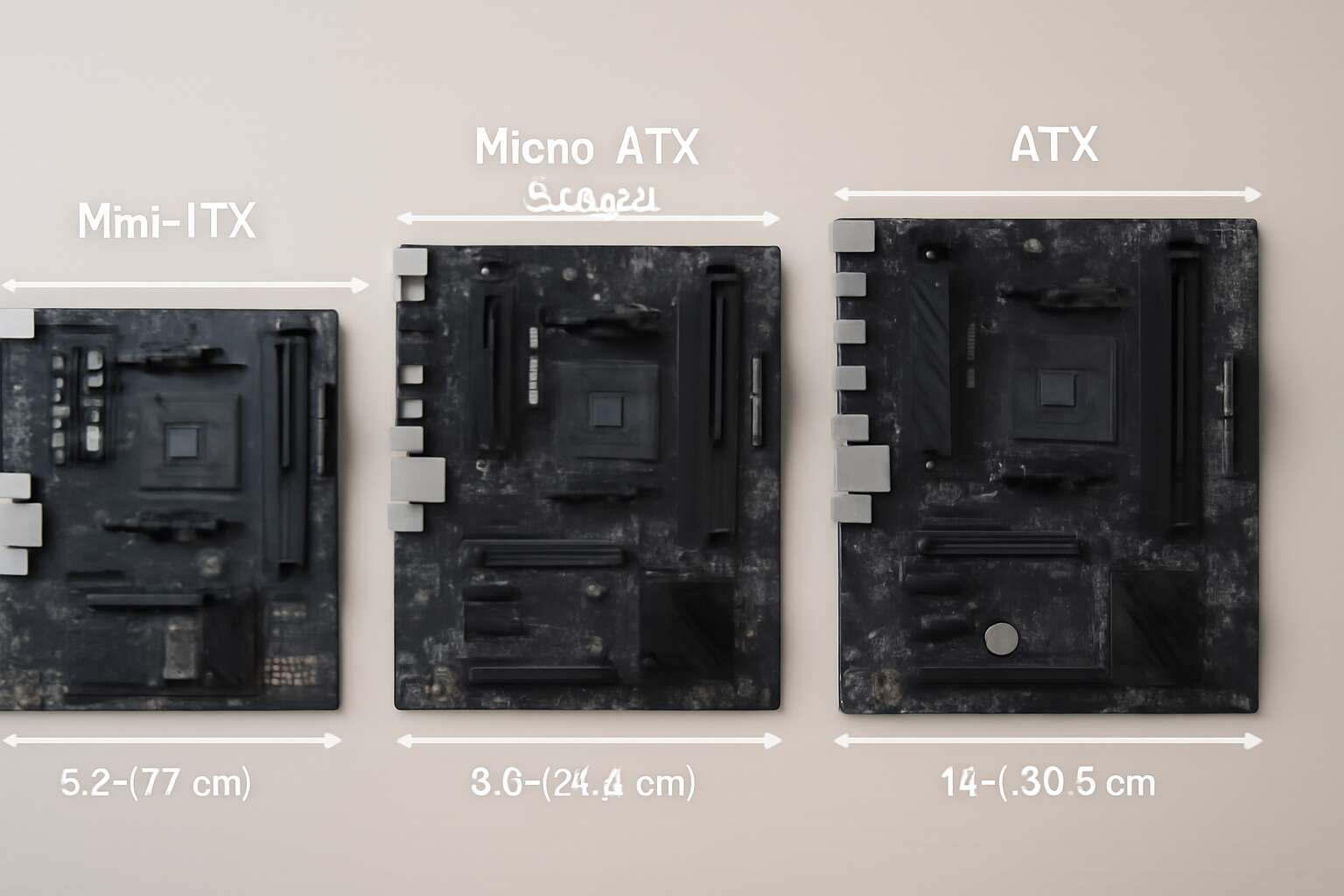
Motherboard sizes are the silent architects of the digital realm, shaping the very backbone of your computing universe. When navigating the labyrinth of options, understanding the standard dimensions of motherboards becomes essential for forging the perfect build. Among these, the ATX motherboard stands tall like a regal citadel, measuring 305mm x 244mm, offering a spacious terrain for expansive configurations and high-end components.
Contrasting this grandeur is the Micro-ATX, a nimble yet powerful contender, with dimensions of 244mm x 244mm. This size balances compactness with versatility, ideal for those seeking a smaller footprint without sacrificing performance. To visualize their differences, consider the following:
- ATX: 305mm x 244mm — the king of size, offering maximum expansion.
- Micro-ATX: 244mm x 244mm — a balanced and space-efficient alternative.
These standard dimensions form the core of motherboard sizes, guiding builders through the intricate dance of component compatibility and spatial constraints. Whether crafting a mighty gaming rig or a sleek workstation, understanding these size comparisons unlocks a world of possibilities in motherboard sizes, ensuring your system is both powerful and harmonious within its case.
Mini-ITX Dimensions – Compact Size Overview
Within the realm of motherboard sizes, the smallest yet most mighty contender is the Mini-ITX. Imagine a tiny fortress, no larger than a paperback, yet housing the core of your digital kingdom. With dimensions of just 170mm x 170mm, Mini-ITX motherboards are crafted for those who seek the ultimate in space efficiency without sacrificing performance. This compact size transforms even the most modest cases into potent machines, perfect for gamers and enthusiasts who crave power in a pint-sized package.
Size comparisons reveal a fascinating spectrum of motherboard sizes, each tailored to specific needs and visions. For instance, while ATX motherboards extend to 305mm x 244mm, offering maximum expansion, Mini-ITX motherboards shrink dramatically, fitting snugly into cases less than half that size. This vast difference highlights the incredible versatility of motherboard sizes available today.
- Mini-ITX: 170mm x 170mm — the compact marvel for small form factor PCs.
- Micro-ATX: 244mm x 244mm — a balanced choice for versatility and space-saving.
- ATX: 305mm x 244mm — the spacious giant for high-end configurations.
Understanding these dimensions unlocks a world where creativity and efficiency collide. Whether you’re building a sleek, portable workstation or a powerhouse gaming rig, the dimensions of your motherboard shape every aspect of your digital adventure, guiding you through the enchanting labyrinth of motherboard sizes with clarity and confidence.
E-ATX Dimensions – Larger Motherboards for Advanced Setups
When visualizing the landscape of motherboard sizes, it’s akin to exploring a diverse ecosystem—each form factor serving a unique purpose and niche. Larger motherboards like the E-ATX, or Extended ATX, are the giants in this realm, measuring up to 305mm x 330mm. These expansive boards are designed for advanced setups, offering extensive expansion slots, multiple GPU support, and superior cooling options. Their size is not just a matter of spatial footprint but a gateway to unrestrained performance, perfect for high-end gaming and professional workstations.
To appreciate the variety, consider the following:
- The E-ATX’s generous dimensions accommodate complex configurations, ideal for enthusiasts who demand maximum customization.
- Meanwhile, standard ATX motherboards, measuring 305mm x 244mm, strike a balance between performance and compatibility, making them the versatile backbone of most gaming rigs.
- Understanding these motherboard sizes ensures building a system that fits both your ambitions and your case’s physical constraints.
- Verify case specifications for supported motherboard sizes.
- Measure internal clearance to accommodate larger motherboards like E-ATX.
- Ensure compatibility with your cooling solutions and expansion needs.
- Assess your current hardware needs and future upgrade plans
- Choose a motherboard size that supports your desired expansion options
- Ensure your case can accommodate the physical dimensions of your motherboard
- Expanded PCIe slots
- Multiple RAM slots
- Enhanced cooling support
From the compact charm of Mini-ITX to the commanding presence of E-ATX, each size offers a distinctive character and set of capabilities, shaping the entire digital experience in South Africa’s tech-savvy landscape.
Compatibility Considerations – Case Compatibility and Motherboard Sizes
Motherboard sizes are the backbone of any PC build, dictating not only spatial compatibility but also influencing performance potential. When selecting the right motherboard size, it’s essential to consider the dimensions and how they fit within your chosen case. Larger sizes like E-ATX, with their expansive measurements, demand spacious enclosures but reward enthusiasts with extensive expansion slots and superior cooling options. In contrast, compact options like Mini-ITX provide a streamlined footprint for small form factor PCs, without sacrificing core functionality.
Compatibility considerations extend beyond just fitting the motherboard inside the case; they also involve ensuring that the case supports the specific motherboard size—whether ATX, Micro-ATX, or Mini-ITX. The case’s internal dimensions must align with the motherboard’s dimensions, providing enough clearance for components and airflow. It’s a delicate dance—choosing a motherboard size that aligns with your performance ambitions while fitting comfortably within your case’s physical constraints.
Understanding these size comparisons and dimensions compatibility considerations is vital for assembling a balanced and efficient system—especially when building for the vibrant tech landscape of South Africa, where adaptability and precision drive innovation. Motherboard sizes truly shape the architecture of your digital realm, offering a spectrum from compact elegance to commanding powerhouses.
Choosing the Right Motherboard Size
Budget and Performance Needs – Matching Size with Performance
Choosing the right motherboard sizes often feels like navigating a labyrinth of options, each promising performance and compatibility. When weighing your budget and performance needs, the size of your motherboard becomes a critical factor. Smaller motherboard sizes, such as Mini-ITX, are perfect for compact builds, but they might limit expansion options. Conversely, larger sizes like Extended ATX (E-ATX) cater to high-performance and gaming systems, offering more slots and features.
Understanding your core requirements helps in making a strategic decision. For instance, if maximum upgrade potential is a priority, opting for larger motherboard sizes ensures you won’t be constrained by space. On the other hand, if portability and space-saving are paramount, smaller motherboard sizes can deliver impressive performance without sacrificing mobility. Ultimately, matching size with performance is about aligning your build goals with the inherent capabilities of each motherboard size.
Case Compatibility – Ensuring Fitment
Choosing the right motherboard size isn’t just a matter of fitting components—it’s about ensuring your entire build functions seamlessly within your chosen case. The compatibility between motherboard sizes and cases can make or break your setup, especially if you’re aiming for a sleek, space-efficient design or a high-performance powerhouse. Motherboard sizes such as ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and E-ATX each have distinct dimensions, so understanding these measurements helps you avoid costly mismatches.
When selecting a case, always verify its supported motherboard sizes. Many cases specify compatible sizes, but it’s wise to double-check the form factor and internal dimensions. For example, a Mini-ITX motherboard will fit comfortably in most small form factor cases, but larger motherboards like E-ATX require more spacious enclosures. An overlooked detail often leads to frustration, especially if you’re upgrading or custom-building. To streamline your decision-making process, consider creating a shortlist of case specifications and cross-referencing them with your preferred motherboard sizes.
For those venturing into high-performance or gaming systems, larger motherboards such as E-ATX offer more expansion slots and advanced features. However, these require a case designed to accommodate their dimensions. Conversely, compact builds benefit from smaller motherboard sizes, offering portability and simplicity without sacrificing core performance. Ultimately, aligning your motherboard sizes with case compatibility ensures a hassle-free assembly and optimal airflow, making your build both functional and future-proof.
Upgrade Flexibility – Future Expansion and Compatibility
Motherboard sizes are more than just measurements—they determine how flexible and future-proof your build can be. Opting for a larger motherboard, like E-ATX, provides ample room for additional RAM slots, multiple GPUs, and advanced storage options. This means your system can evolve over time without the need for a complete overhaul. Conversely, smaller motherboard sizes such as Mini-ITX prioritize portability and simplicity but may limit expansion possibilities.
When considering upgrade flexibility, it’s crucial to evaluate your long-term needs. For instance, if you plan to add multiple graphics cards or extra storage drives, a standard ATX or E-ATX motherboard might be the most suitable. On the other hand, if your goal is a sleek, space-efficient build, Micro-ATX offers a good compromise—balancing size and expandability. Remember, compatibility with your chosen case is essential for seamless upgrades, so always cross-check motherboard sizes with your case specifications.
Motherboard sizes influence not just the initial build but also how easily you can adapt and enhance your system later. Whether you’re building a gaming powerhouse or a portable workstation, understanding these dimensions ensures your setup remains compatible, scalable, and ready for whatever the future holds.
Advantages and Limitations of Different Sizes
ATX – Balance of Features and Expandability
Motherboard sizes are more than just a matter of dimensions—they shape the very soul of your computing experience. Among these, ATX motherboards strike a captivating balance of features and expandability. Their generous size allows for multiple PCIe slots, extensive RAM slots, and a plethora of connectivity options, making them a favorite for gamers and power users alike. This versatility ensures that as technology evolves, your motherboard can grow with you, accommodating new components with ease.
However, the expansive nature of ATX motherboards also brings limitations. Larger sizes demand spacious cases and can challenge tight workspace setups. For those seeking a more streamlined build without sacrificing too much functionality, micro-ATX motherboards offer a compelling compromise. They retain several key features of ATX while fitting into smaller cases, but sometimes at the expense of maximum expansion options. The key advantage of ATX motherboards is their ability to provide a robust platform that balances performance, features, and future upgrade potential.
In essence, selecting the right motherboard size is like choosing a vessel for your digital voyage—one that must match your ambitions, space constraints, and upgrade plans. Whether you prioritize expansive feature sets or compact convenience, understanding the advantages and limitations of each size ensures your build is both powerful and harmonious.
Micro-ATX – Space Saving with Adequate Features
Micro-ATX motherboards are a clever solution for those who crave space efficiency without sacrificing essential features. Their compact design enables gamers and tech enthusiasts to build powerful systems within smaller cases, making them ideal for tight workspaces or sleek desk setups. Despite their size, micro-ATX motherboards often include multiple RAM slots and several PCIe expansion slots, offering a surprising level of versatility. This balance of form and function ensures your build can handle high-performance components while remaining streamlined.
However, the advantages of smaller motherboard sizes come with certain limitations. The reduced physical footprint means fewer expansion options compared to larger counterparts like ATX. For instance, micro-ATX motherboards may only support a limited number of graphics cards or storage devices. Yet, this trade-off is often acceptable for users prioritizing space-saving design over maximum upgrade potential. Ultimately, micro-ATX motherboards deliver a harmonious blend of performance and compactness, perfect for those who seek efficiency without compromising on core features.
Mini-ITX – Best for Small Builds, Limited Expansion
Mini-ITX motherboards are the stealthy assassins of the PC world—small, powerful, and ready to take on the tightest of spaces. Ideal for small form factor PCs, they pack a punch despite their diminutive size. Their compact footprint makes them perfect for users who crave portability without sacrificing core performance. But beware—these tiny titans come with limitations that can’t be ignored.
One of the main disadvantages of smaller motherboard sizes is limited expansion. Mini-ITX boards typically feature only one PCIe slot and a handful of RAM slots, restricting future upgrades. This can be a dealbreaker for gamers or professionals aiming to upgrade graphics cards or storage over time. Yet, their streamlined design offers a clean, clutter-free build that’s especially appealing in ultra-compact cases.
For those who need to balance size and functionality, understanding the trade-offs of motherboard sizes is crucial. Mini-ITX offers unmatched space-saving benefits but at the expense of expansion potential. It’s a choice that demands strategic planning—making every component count in the shadowy world of small builds. When space is at a premium, the advantages of small motherboard sizes become unmistakably clear, even if their limitations are just as apparent.
E-ATX – High-End Performance with Extensive Expansion Options
E-ATX motherboards are the giants of the motherboard sizes, offering high-end performance combined with extensive expansion options. These large boards are designed for enthusiasts and professionals who demand maximum capability from their systems. With multiple PCIe slots and abundant RAM slots, E-ATX boards support complex setups—think multiple graphics cards or advanced storage arrays.
One of the main advantages of this motherboard size is its flexibility. You can install sophisticated cooling solutions, multiple NVMe drives, and even custom water cooling loops. For users aiming to build a powerful gaming rig or a workstation, E-ATX provides the space needed for future upgrades and tweaks.
However, these benefits come with limitations. E-ATX motherboards require larger cases, which may not fit in standard or compact setups. They also tend to be more expensive and consume more power. For those prioritizing a sleek, space-saving build, the size of motherboards in this category can be a significant drawback. Ultimately, the choice depends on balancing the desire for performance against physical and budget constraints within the realm of motherboard sizes.
Popular Uses for Various Motherboard Sizes
Gaming PCs – Choosing the Best Size for Performance
When it comes to building a gaming PC, selecting the optimal motherboard sizes can be a game-changer. Different sizes cater to distinct performance needs and spatial constraints, making the decision an intricate dance between power and practicality. For high-end gaming systems demanding extensive expansion, the Extended ATX (E-ATX) motherboard sizes are often the go-to choice. These larger boards provide ample space for multiple GPUs, advanced cooling solutions, and a plethora of PCIe slots, ensuring no performance bottleneck occurs.
However, if space efficiency is paramount, Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX motherboard sizes excel in delivering adequate features within a compact footprint. Micro-ATX offers a balanced approach—enough expansion options without sacrificing too much room. Mini-ITX, on the other hand, is perfect for small form factor PCs, blending portability with surprisingly robust performance capabilities. Understanding the nuanced differences between motherboard sizes allows enthusiasts to tailor their build precisely to their gaming aspirations and spatial limitations.
Workstations – Motherboard Sizes for Heavy-Duty Tasks
Motherboard sizes are the unsung heroes of heavy-duty workstations, quietly dictating what kind of beast you can build. When tackling intensive tasks like 3D rendering, scientific simulations, or complex data analysis, choosing the right motherboard size becomes crucial. Larger formats like Extended ATX (E-ATX) provide the sprawling real estate needed for multiple high-speed storage drives, extensive PCIe slots, and advanced cooling solutions—think of it as the luxury mansion of motherboards. These sizes are perfect for those who refuse to compromise on performance or expandability.
For demanding workloads, the size does matter. A well-chosen motherboard size can mean the difference between a sluggish build and a powerhouse ready to conquer heavy-duty tasks with ease. Whether it’s the expansive E-ATX or the more modest Micro-ATX, understanding the nuances of motherboard sizes helps tailor your workstation to your specific needs—because in the world of heavy lifting, size does count!
Home Theater and Small Form Factor PCs – Mini and Micro Sizes
Motherboard sizes play a pivotal role in shaping the perfect home theater or small form factor PC. These compact models, like Mini-ITX and Micro-ATX, are designed with space efficiency in mind. They fit snugly into small cases, making them ideal for entertainment systems that don’t compromise on performance. Mini-ITX, in particular, is prized for its tiny footprint—perfect for discreet setups that blend seamlessly into any living room.
For users prioritizing a clutter-free environment without sacrificing power, Micro-ATX offers a sweet spot. It provides enough expansion slots for essential components while maintaining a compact form. These motherboard sizes are often used in small PCs where space is limited but reliable performance is non-negotiable. Whether you’re building a sleek media centre or a compact gaming rig, understanding motherboard sizes ensures your system fits perfectly without limiting future upgrades.
Future Trends in Motherboard Sizes
Design Innovations – Growing Needs for Compact Yet Powerful Boards
As technology relentlessly pushes boundaries, future trends in motherboard sizes are poised for a fascinating evolution. The growing demand for compact yet powerful boards reflects our collective desire for efficiency without sacrificing performance. It’s no longer enough to have a motherboard that simply fits; it needs to optimize space while supporting cutting-edge components. This shift towards miniaturization is driven by innovations in design technology, where engineers are developing smaller, more integrated motherboard sizes that do not compromise on features.
One compelling trend is the rise of ultra-compact motherboards that maintain high performance levels—ideal for those who seek portability without surrendering upgrade potential. We’re also witnessing a surge in modular designs that allow for tailored configurations, creating a new paradigm of flexibility in motherboard sizes. For example, some manufacturers are experimenting with layered architectures and advanced cooling solutions to maximize the utility of smaller form factors.
In tandem with these innovations, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on compatibility and ease of integration, recognizing that the future of motherboard sizes lies in versatile, adaptable designs. As the digital landscape evolves, so too will these boards—becoming sleeker, smarter, and more attuned to the needs of South African tech enthusiasts. The promise of future motherboard sizes is a landscape where size and power are no longer mutually exclusive but harmoniously intertwined.
Custom and Niche Sizes – Emerging Form Factors for Specialized Builds
As technology continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, the future of motherboard sizes is becoming more tailored and innovative than ever. Custom and niche sizes are emerging to meet the specific demands of specialized builds, from ultra-compact servers to high-performance workstations. These emerging form factors challenge traditional boundaries, offering unprecedented flexibility for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
One notable trend is the rise of bespoke motherboard sizes designed for particular applications. For instance, custom-sized boards are now crafted for compact AI rigs, embedded systems, or even niche gaming setups that require unique spatial configurations. These specialized sizes often incorporate layered architectures or modular components, allowing for seamless upgrades and tailored performance without sacrificing form factor constraints.
In South Africa, where space optimization is often a necessity, these niche motherboard sizes are opening new doors for affordable, efficient computing solutions. As the digital landscape becomes more diverse, the need for adaptable, purpose-built motherboards continues to grow. With each innovation, motherboard sizes become less about fitting into predefined categories and more about creating a harmonious balance between size, power, and future expansion.



0 Comments