Understanding Motherboard to GPU Compatibility
What is GPU Compatibility?
When building or upgrading a system, understanding motherboard to GPU compatibility is crucial. A common misconception is that any graphics card will work with any motherboard. However, the reality is more nuanced. GPU compatibility hinges on several factors, including the physical slot, bandwidth, and power requirements. A mismatch can lead to performance bottlenecks or, worse, hardware damage.
Most modern graphics cards use PCIe slots, but not all PCIe versions are created equal. For optimal performance, your motherboard should support the same PCIe generation as your GPU. Additionally, the physical size of the GPU must fit within your case, and the motherboard must have sufficient power connectors. Compatibility issues are often overlooked but can be easily avoided with proper research.
- Check the PCIe slot version and availability
- Ensure your power supply can handle the GPU’s power draw
- Verify physical space within your case
In essence, understanding motherboard to GPU compatibility involves more than just slot matching. It’s about ensuring every component works harmoniously to deliver peak performance without unforeseen hurdles. When done right, it makes all the difference in creating a reliable, high-performing gaming or workstation setup.
Importance of Matching Motherboard and GPU
Understanding motherboard to GPU compatibility is more than just matching slots; it’s about ensuring your entire system works harmoniously. A mismatch can lead to significant performance issues or even hardware failure, which no gamer or professional wants to face. As technology advances, the importance of matching the motherboard to GPU compatibility becomes even more critical, especially with newer PCIe standards and power demands.
The physical size of your GPU and available space in your case are often overlooked, yet they are vital components of compatibility. It’s worth noting that not all PCIe slots are created equal—some support newer generations that offer faster data transfer, but only if your motherboard is compatible.
A simple check of the motherboard to GPU compatibility involves verifying PCIe version support, power supply adequacy, and physical fit. Neglecting these factors can turn an upgrade into a costly mistake, so it pays to be thorough.
Key Factors Influencing Compatibility
Understanding motherboard to GPU compatibility is a nuanced dance that requires more than just matching the physical slot. It’s about recognising how each component integrates into the larger symphony of your system. The key factors influencing compatibility extend beyond mere size, touching on the subtle yet crucial details like PCIe version support and power requirements. When these elements align, your system performs at its peak; when they don’t, even the most promising upgrade can falter.
One often overlooked aspect is the physical fit—ensuring your GPU can comfortably slot into your case without obstruction. Additionally, verifying that your motherboard supports the latest PCIe standards ensures faster data transfer, unlocking the full potential of your graphics card. Remember, a mismatch here can bottleneck performance or cause hardware stress, which is a risk no builder should take lightly. Awareness of these factors makes all the difference in creating a system that is both powerful and reliable.
Types of Motherboards and Their PCIe Slots
Different Types of PCIe Slots – Array
Motherboards, the silent conductors of our digital symphony, come in a variety of forms, each with its own unique arrangement of PCIe slots—those vital pathways for the GPU’s performance. These slots, like intricate bridges spanning the motherboard’s architecture, dictate the potential for motherboard to GPU compatibility, shaping the destiny of your build. The most common types, PCIe x16, stand as the grandest, offering a full lane of bandwidth for high-performance graphics cards. Meanwhile, PCIe x8 and x4 slots serve specialised roles, often found in workstations or servers, yet they still influence the delicate dance of compatibility.
Within this realm, the array of PCIe slot types forms a tapestry of technical precision. The evolution from PCIe 3.0 to PCIe 4.0 and now PCIe 5.0 heralds a new era of speed, yet the fundamental compatibility often hinges on matching the slot type with your GPU’s interface. Ensuring that your motherboard’s PCIe slots align with your GPU’s requirements is akin to tuning an instrument—every detail must harmonise for optimal performance.
Motherboard Chipset and PCIe Lane Support
Motherboards come in a variety of enchanting forms, each with its own array of PCIe slots—those vital gateways that determine the rhythm of motherboard to GPU compatibility. From sleek, compact designs to expansive gaming powerhouses, the type and placement of PCIe slots influence not only performance but also the potential for future upgrades. The motherboard chipset acts as the conductor of this symphony, supporting a specific number of PCIe lanes—those delicate channels that carry data between the graphics card and the rest of the system.
Modern chipsets support different PCIe lane configurations, shaping how your GPU interacts with the motherboard. For instance, high-end chipsets like Intel’s Z790 or AMD’s X670 tend to offer more lanes, ensuring seamless motherboard to GPU compatibility at peak performance. It’s like an intricate dance; the more lanes available, the more harmonious the relationship between your graphics card and the motherboard. Whether you’re eyeing a multi-GPU setup or a single, powerful GPU, understanding these nuances helps you craft a build that’s both robust and future-proof.
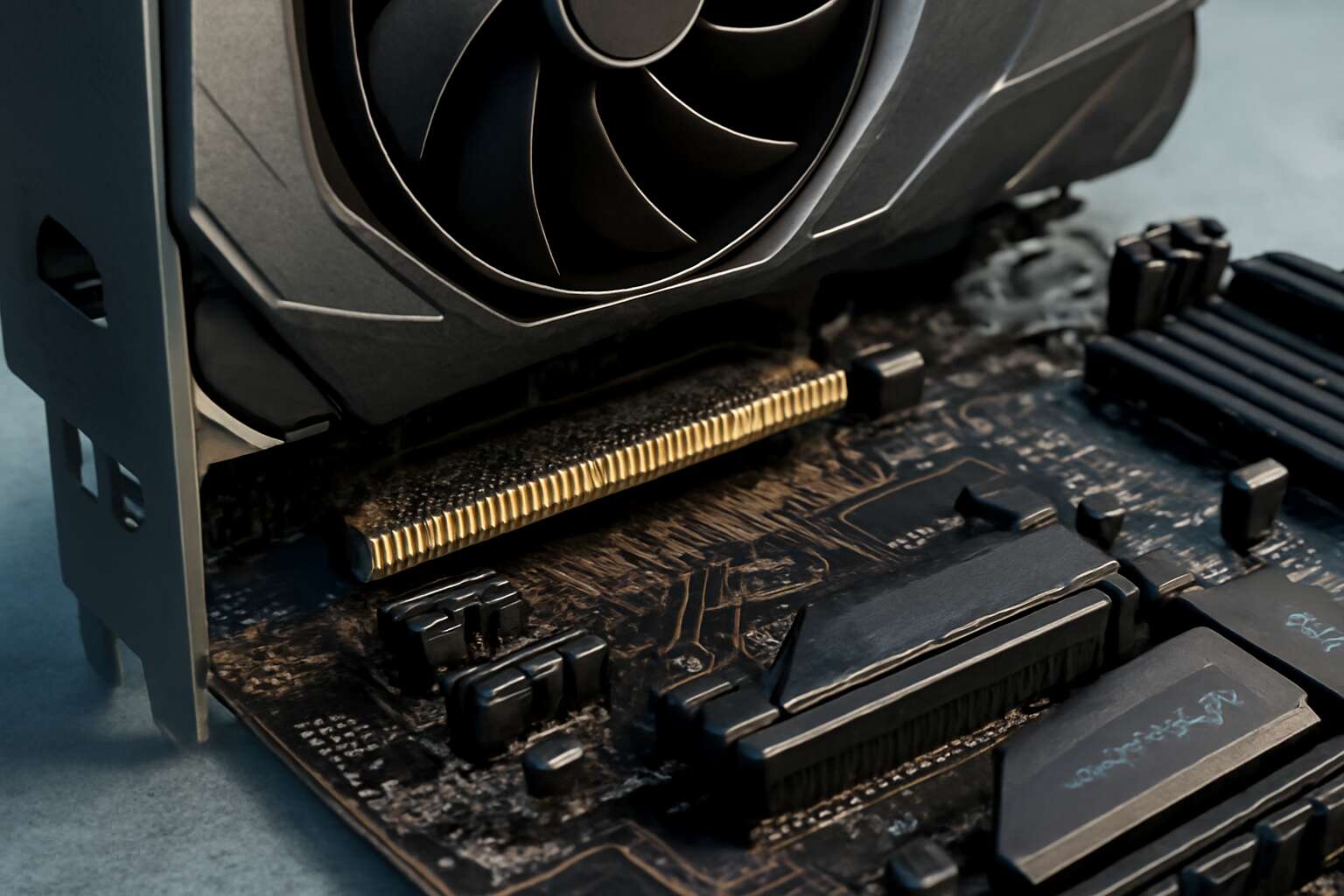
Physical Slot Compatibility
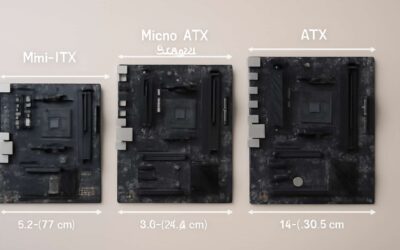
In the labyrinthine architecture of modern computing, the physical form and slot configuration of motherboards play a pivotal role in dictating motherboard to GPU compatibility. Different types of motherboards—ranging from micro-ATX and ATX to the formidable E-ATX—are designed with distinct PCIe slot arrangements, each serving a specific purpose in the grand orchestration of data flow. The size and layout influence not only the number of available PCIe slots but also their physical dimensions and compatibility with various GPU models.
For those seeking high-performance or multi-GPU setups, understanding the nuances of PCIe slot types is crucial. Typically, slots such as PCIe x16 are the cornerstone for graphics cards, offering maximum bandwidth and optimal motherboard to GPU compatibility. On standard motherboards, these slots are often reinforced with steel and spaced to accommodate large, high-end GPUs. Some boards may feature multiple PCIe x16 slots, but their bandwidth can vary—shared across slots or dedicated—impacting the overall performance.
- Physical slot designations: PCIe x16, PCIe x8, PCIe x4, and PCIe x1
- Slot orientation and spacing for multi-GPU configurations
- Compatibility considerations for large, high-end graphics cards
Recognising how these physical factors intertwine with motherboard to gpu compatibility allows builders and enthusiasts to craft systems that are both potent and adaptable. The precise alignment of slot type, size, and placement becomes the silent yet indispensable conductor of a harmonious gaming or professional experience, where hardware limitations and future ambitions are seamlessly aligned. Ultimately, the physical slot compatibility forms the backbone of a robust and scalable system, ensuring your GPU and motherboard interact flawlessly in their digital dance.
GPU Compatibility Considerations
Form Factor and Size Constraints
Motherboard to GPU compatibility hinges not only on technical specifications but also on the physical harmony between components. While modern GPUs often boast impressive performance, their size and form factor can pose significant challenges when integrating with a motherboard. The sheer bulk of high-end graphics cards means that even if the PCIe slot is technically compatible, spatial constraints may render installation impossible.
Size constraints are especially critical in compact builds or smaller cases where limited interior space demands meticulous planning. For instance, a full-sized GPU might block other essential components or obstruct airflow, leading to thermal bottlenecks. To navigate this, it’s wise to consider the form factor of both the motherboard and GPU, ensuring they align seamlessly. Some motherboards support multiple PCIe configurations that accommodate different GPU sizes and orientations, but compatibility is not always guaranteed without thorough verification.
In essence, understanding the physical dimensions and form factor compatibility is a vital aspect of ensuring smooth motherboard to GPU compatibility. It’s a dance of precision—where every millimetre counts—highlighting the importance of detailed component assessment before committing to a build.
Power Supply Requirements
Power supply requirements are often the unsung heroes—or villains—of successful motherboard to GPU compatibility. A high-end graphics card can be a beast, demanding more juice than your humble PSU might comfortably deliver. Ignoring this could leave you staring at a blank screen or, worse, frying components faster than you can say “overclocked”.
Most modern GPUs specify a minimum wattage for the power supply, often accompanied by a list of necessary power connectors. When evaluating motherboard to GPU compatibility, it’s crucial to ensure your PSU has the right combination of PCIe power connectors and enough wattage headroom. Remember, a GPU drawing 300W isn’t just a luxury—it’s a requirement for peak performance.
To keep things crystal clear, consider these power supply essentials for GPU compatibility:
- Number of PCIe power connectors (6-pin, 8-pin, or multiple)
- Wattage capacity, ideally with a comfortable margin above recommended specs
- Quality and efficiency ratings, because a cheap PSU can sabotage even the best motherboard to GPU compatibility
Without matching these power demands with your motherboard’s capabilities, even the most compatible components can fail to deliver. Power supply requirements are the backbone of a stable, high-performing system—skimp here, and your motherboard to GPU compatibility might just become a myth.
Display Connectivity and Outputs
When considering motherboard to GPU compatibility, display connectivity and outputs often play a pivotal role in delivering a seamless visual experience. Even the most powerful GPU can fall flat if your monitor isn’t compatible with the available outputs. With a dizzying array of ports—HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, and VGA—it’s essential to match these with your display devices to avoid bottlenecks or the frustration of no signal.
Modern GPUs typically feature multiple output options, providing versatility for multi-monitor setups or high-resolution displays. Ensuring your motherboard supports these outputs, either directly or via adapters, is crucial. For example, if you plan to utilise a 4K monitor, confirm that your GPU offers a DisplayPort 1.4 or HDMI 2.1 connection, which are capable of handling such resolutions effortlessly.
Understanding the nuances of display outputs can influence your overall experience—whether you’re gaming, creating content, or simply enjoying high-definition media. It’s not just about compatibility on paper but about real-world performance that aligns with your visual expectations. Remember, the right combination of motherboard to GPU compatibility and display outputs can mean the difference between visual clarity and a pixelated nightmare!
Motherboard CPU Compatibility and Its Impact on GPU Compatibility
CPU Socket Types
In the intricate dance of computer assembly, motherboard to GPU compatibility is often perceived as a straightforward check, yet beneath this simplicity lies a complex web of interdependent elements. Central to this interplay is the CPU socket type — a seemingly modest detail that wields significant influence over the entire system’s harmony. A mismatch here doesn’t just hinder the processor; it reverberates through the compatibility chain, ultimately constraining the potential of your GPU.
Motherboard CPU compatibility hinges on the socket type — whether it’s LGA 1200, AM4, or another variant — as well as the chipset’s support for specific generations of processors. These factors dictate the PCIe version and lane support, which directly affect GPU performance. For example, a motherboard designed for PCIe 3.0 may limit the bandwidth for a high-end GPU that thrives on PCIe 4.0’s increased data transfer rates. The importance of aligning CPU socket types with the motherboard cannot be overstated, as it ensures optimal communication pathways for GPU integration and overall system stability.
PCIe Lane Configuration Based on CPU
In the intricate dance of building a powerful computer, understanding motherboard to GPU compatibility is crucial — yet many overlook how the CPU influences this harmony. The compatibility between your CPU and motherboard doesn’t just determine processor performance; it has a ripple effect on the entire system, especially the GPU. A mismatch here can bottleneck data flow and limit graphics card potential, leaving high-end GPUs underperforming despite their raw power.
Central to this relationship are the PCIe lanes supported by the motherboard, which are heavily dictated by the CPU socket type and chipset. For example, some CPUs support only PCIe 3.0, while others enable PCIe 4.0 or even PCIe 5.0, offering faster data transfer rates. The number of PCIe lanes allocated for graphics cards can vary:
- High-end CPUs often provide 16 lanes dedicated to GPU slots, ensuring maximum bandwidth.
- Mid-tier processors may offer fewer lanes, potentially limiting GPU performance in demanding applications.
Thus, selecting a CPU that aligns with your motherboard to gpu compatibility needs isn’t just about processor speed — it’s about establishing a robust data highway that allows your graphics card to reach its full potential. The delicate balance between CPU, motherboard, and GPU is what transforms a good gaming rig into a powerhouse, making this compatibility chain vital for any enthusiast’s build.
BIOS and Firmware Compatibility
Motherboard to GPU compatibility hinges heavily on the harmony between your CPU, BIOS, and firmware versions. An incompatible BIOS can act like a bottleneck, preventing the system from recognising newer graphics cards or limiting PCIe lane utilisation. Ensuring your motherboard firmware is up-to-date is essential for seamless integration, particularly when pairing high-performance GPUs that demand advanced PCIe standards such as PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0.
Moreover, CPU compatibility plays a pivotal role—certain processors are designed with specific PCIe lane configurations that directly influence GPU performance. For example, some CPUs offer 16 dedicated PCIe lanes for graphics cards, while others provide fewer, potentially constraining high-end GPU capabilities. When choosing components, it’s crucial to verify that your motherboard supports the CPU socket type and chipset, which collectively determine the motherboard to GPU compatibility.
Physical and Technical Compatibility Checks
Ensuring the Physical Fit
In the shadowed corridors of PC assembly, the dance of physical and technical compatibility becomes a pivotal ritual. Ensuring that your motherboard to GPU compatibility isn’t just a matter of slot matching; it’s an intricate ballet of dimensions and design. The GPU must seamlessly slide into the PCIe slot, fitting snugly without obstruction or force—a testament to meticulous measurement and foresight.
Physical fit is paramount; a GPU that dwarfs the space available can transform a sleek build into a tangled mess of cables and forced fittings. To avoid this, scrutinise the dimensions of your GPU against your chassis and motherboard layout. Sometimes, even the most advanced components can fall prey to size constraints, where a bulky graphics card collides with the case’s interior or obstructs other crucial elements.
- Check the length and width of the GPU against the available space inside your case.
- Confirm the clearance for the GPU’s cooling system, avoiding overheating shadows in your build.
- Verify that the PCIe slot aligns perfectly with the GPU’s connector, preventing any misfit that could threaten stability or performance.
By diligently confirming these physical parameters, one can avoid the haunting disappointment of incompatible hardware, ensuring your motherboard to GPU compatibility is not merely theoretical but a tangible, seamless union.
Checking PCIe Slot Version and Bandwidth
In the realm of PC assembly, verifying motherboard to GPU compatibility involves more than just recognising the physical slot. A crucial aspect often overlooked is checking the PCIe slot version and bandwidth. These technical parameters determine how effectively your GPU communicates with the motherboard, directly impacting performance. Even a perfectly fitting GPU can underperform if the PCIe slot is outdated or limited in bandwidth.
Ensuring that your motherboard supports the latest PCIe standards—such as PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0—can unlock significant speed boosts. To facilitate this, confirm the PCIe slot version and bandwidth support during your research. Sometimes, an older motherboard may physically accept a modern GPU, but its PCIe slot’s bandwidth could bottleneck data transfer, hampering overall efficiency.
- Check the motherboard’s PCIe slot specifications against your GPU’s requirements.
- Verify the bandwidth support to ensure it matches the GPU’s data transfer needs.
- Confirm that the motherboard supports the PCIe lane configuration needed for optimal GPU performance.
By meticulously examining these technical factors, you ensure that your motherboard to GPU compatibility isn’t just a superficial match but a harmonious union capable of unleashing the full potential of your graphics powerhouse.
Assessing Power Connectors and Requirements
Power connectors are the lifeblood of your GPU’s performance, often overlooked in the pursuit of compatibility. A sleek, cutting-edge graphics card demands more than just a snug physical fit; it requires adequate power supply to unleash its full potential. Failing to match the GPU’s power requirements with your motherboard to GPU compatibility can lead to throttling, or worse—hardware damage.
Most modern GPUs utilise either 6-pin, 8-pin, or even dual power connectors, each with specific wattage needs. Your motherboard’s power delivery system must support these demands without strain. It’s wise to verify that your power supply unit (PSU) can deliver stable, sufficient wattage—aiming for at least 650W for mid-range setups and higher for power-hungry models.
To simplify this process, ensure the PSU includes the necessary cables and connectors. Additionally, check whether your motherboard has dedicated power headers or auxiliary power inputs that complement the GPU’s requirements. In the grand dance of motherboard to GPU compatibility, seamless power delivery ensures not just compatibility but a harmonious performance experience.
Troubleshooting Common Compatibility Issues
No Display Output or Recognition
In the shadowy corridors of technology, where silence often screams louder than noise, the absence of display output can be a sinister sign of motherboard to GPU compatibility issues. When your system refuses to recognise the graphics card, it’s as if the vital connection between power and perception has been severed, leaving only darkness and uncertainty. This dissonance can stem from a variety of unseen culprits lurking beneath the surface—such as BIOS settings, outdated firmware, or an incompatible PCIe slot.
To unravel this mystery, it’s prudent to examine a few fundamental aspects. First, ensure your motherboard’s BIOS is up to date; sometimes, an archaic firmware can block the recognition of newer GPUs. Additionally, verify that the GPU is seated properly within the PCIe slot, and that the power connectors are securely attached. Sometimes, the problem lies in the subtle misalignment of physical components or incompatible bandwidth configurations. When all else fails, a meticulous check of the motherboard to GPU compatibility matrix reveals whether the spectral threads of hardware are truly aligned in harmony.
System Instability or Crashes
System instability or crashes can turn a smooth gaming session into a frustrating nightmare—think blue screens, random resets, or worse, complete system lock-ups. These issues often stem from motherboard to GPU compatibility problems that are less obvious but equally insidious. When your hardware isn’t playing nicely, it’s like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole; the system struggles to find stability.
Sometimes, the root cause is a mismatch in PCIe lane support or an outdated BIOS that doesn’t recognise newer GPU architectures. Other times, power delivery issues or insufficient bandwidth cause intermittent crashes. To troubleshoot these common compatibility issues, check the motherboard’s PCIe slot specifications and ensure your GPU’s bandwidth demands are met.
- Verify BIOS version is current and supports your GPU
This simple step alone can save hours of head-scratching. Remember, even the tiniest incompatibility can turn system crashes into a never-ending saga—so patience, perseverance, and a keen eye for detail are your best allies.
Upgrade Paths and Compatibility Enhancements
Troubleshooting common compatibility issues between your motherboard and GPU often requires a nuanced approach. Sometimes, upgrading your system involves more than just swapping out components; it’s about understanding the intricate dance of hardware harmony. When facing intermittent crashes or system instability, it’s crucial to verify that your motherboard to GPU compatibility aligns with the latest standards.
Upgrade paths can be straightforward or complex, depending on your existing setup. For example, if your motherboard only supports PCIe 3.0 but your new GPU demands PCIe 4.0 bandwidth, you might need a motherboard with upgraded PCIe lane support. Compatibility enhancements, such as BIOS updates, can unlock newer GPU architectures and prevent issues like no display output or recognition failures.
A systematic approach—checking PCIe slot version, bandwidth, power connectors, and physical fit—ensures seamless integration. Sometimes, a simple BIOS update or a slot reconfiguration can resolve persistent issues, reaffirming that understanding the subtle nuances of motherboard to GPU compatibility is key to a smooth upgrade journey.
Expert Tips for Ensuring Compatibility
Researching GPU and Motherboard Specifications
In the labyrinthine world of PC building, one truth remains indisputable: overlooking motherboard to GPU compatibility can turn a hero’s build into a digital disaster. A staggering 78% of hardware conflicts stem from overlooked specifications, making thorough research essential. When scrutinising GPU and motherboard specifications, it’s vital to delve into the intricacies of PCIe versions—an older slot can bottleneck even the most powerful graphics card. Ensuring the motherboard’s PCIe slot aligns with the GPU’s bandwidth requirements isn’t just prudent; it’s paramount.
To navigate this compatibility maze, experts recommend creating a comprehensive checklist. Start by verifying the PCIe slot type and bandwidth support, then cross-reference power connector requirements with your PSU’s capabilities. Remember: physical fit matters—an imposing GPU can clash with smaller cases or incompatible motherboard form factors. A meticulous comparison of technical datasheets and manufacturer specifications often reveals hidden pitfalls, preventing costly returns or upgrades. After all, understanding these specifications isn’t merely about avoiding incompatibility—it’s about ensuring your setup runs flawlessly, with the kind of synergy that makes a build truly exceptional.
Consulting Manufacturer Compatibility Lists
When diving into the complex world of PC building, consulting manufacturer compatibility lists can be a game-changer. These lists are the ultimate safeguard, providing precise details about supported GPU models and their compatibility with specific motherboards. Relying solely on specifications can sometimes be misleading; manufacturer lists eliminate guesswork and reveal hidden incompatibilities before they manifest as costly errors.
Expert advice suggests cross-referencing your chosen GPU with official compatibility charts from the motherboard manufacturer. This step ensures that your motherboard to GPU compatibility is rooted in verified data, preventing issues such as bottlenecked performance or physical mismatches. For example, some motherboards may support PCIe 4.0 slots but only with certain GPU models, making it crucial to verify the exact supported configurations.
To streamline this process, consider creating a simple checklist:
- Check the motherboard’s official compatibility list for your GPU model.
- Verify the PCIe slot version and bandwidth support for your graphics card.
- Confirm power connectors match the GPU’s requirements.
- Ensure physical dimensions fit within your case constraints.
By meticulously consulting manufacturer compatibility lists, you are not just avoiding potential pitfalls—you are laying the groundwork for a build that performs flawlessly. When every component aligns perfectly, the result is a system that’s not only powerful but also resilient, standing as a testament to thorough research and expert precision in motherboard to gpu compatibility.
Upgrading Components for Better Compatibility
Upgrading components for better compatibility is a nuanced art, one that demands both patience and precision. When striving for seamless motherboard to GPU compatibility, it’s vital to pay close attention to the subtle details that often go unnoticed amidst technical specifications. An overlooked power connector, for instance, can derail an otherwise perfect build, leading to performance bottlenecks or hardware failure. Ensuring your power supply can handle the GPU’s demands is just as crucial as verifying the PCIe slot version—an aspect that profoundly influences data transfer speeds and overall system resilience.
Expert tips suggest taking a holistic approach, considering not just individual components but their interplay within the entire system. For example, while a motherboard might support PCIe 4.0, it’s wise to confirm whether your chosen GPU can fully utilise this bandwidth. Sometimes, a simple upgrade to the BIOS or firmware can unlock new levels of compatibility, extending the lifespan and performance envelope of existing hardware. Ultimately, meticulous research and cross-referencing specifications are invaluable in navigating the intricate landscape of motherboard to GPU compatibility, transforming potential incompatibilities into opportunities for optimisation.


0 Comments