Understanding Motherboard Generations
Overview of Motherboard Evolution – A brief history of motherboard development
Motherboard technology has evolved at a breathtaking pace, mirroring the relentless pursuit of innovation in the digital age. The question of how many motherboard generations are there is fascinating, as it reflects decades of relentless advancement from simple circuitry to sophisticated architectures that power our modern world. Each generation signifies a leap forward in connectivity, speed, and versatility, capturing the spirit of technological progress.
From the earliest days of PC development, motherboard generations have marked distinct milestones. For example, the transition from the revolutionary ATX standard to the more recent PCIe 4.0 and 5.0 architectures illustrates the continuous pursuit of higher data transfer rates and improved stability. Understanding this evolution offers a window into the intricate dance of hardware innovation and the ever-expanding capabilities of computers.
In fact, the history of motherboard development can be summarised through key phases, each characterised by unique features and technological breakthroughs:
- Introduction of ISA and PCI slots
- Emergence of DDR RAM standards
- Adoption of advanced chipset architectures
- Transition from AGP to PCI Express
As we explore how many motherboard generations are there, it becomes clear that each iteration not only embodies technological progress but also shapes how we interact with digital environments. The journey from early motherboard designs to the cutting-edge platforms of today encapsulates a story of relentless human ingenuity and the pursuit of perfection in computing hardware.
What Defines a Motherboard Generation – Key technological features and standards
Ever wondered how many motherboard generations are there? The answer might surprise you — or at least make you realise just how swiftly technology evolves. A motherboard isn’t just a static piece of hardware; it’s a living, breathing testament to our relentless quest for speed, stability, and connectivity. Each generation introduces a new set of technological features that push the boundaries of what’s possible.
What exactly defines a motherboard generation? It’s not just about the number of USB ports or the colour scheme. Instead, it revolves around key technological standards that mark a paradigm shift. For example, the advent of DDR RAM standards brought a significant leap in memory speed, while the transition from PCI to PCIe (PCI Express) revolutionised data transfer rates. These milestones are the pillars of what makes each generation distinct, often accompanied by innovations such as advanced chipset architectures and improved power delivery systems.
To grasp the full scope, consider this: each new motherboard generation introduces a combination of features that can be summarised as follows:
- Introduction of new expansion slots — from ISA to PCI, then PCIe
- Support for faster RAM standards such as DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5
- Enhanced chipset architectures for better stability and connectivity
- Improved integration of peripherals and onboard components
Understanding how many motherboard generations are there requires recognising that each iteration isn’t merely incremental; it’s a leap forward in the ongoing saga of hardware innovation. The evolution continues, with each generation promising faster, more reliable, and more versatile platforms that keep our digital lives spinning smoothly. Truly, it’s a journey driven by human ingenuity — and a relentless pursuit of perfection in hardware design.
Importance of Knowing Different Generations – Choosing the right motherboard for your needs
Understanding motherboard generations is crucial when navigating the ever-evolving landscape of computer hardware. With each new wave of innovation, knowing how many motherboard generations are there can make or break your build — or at least prevent you from buying a relic that’s only good for nostalgia.
Motherboard generations are not just about shiny new features; they’re about aligning your system with the latest standards in connectivity, speed, and stability. Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or someone who simply wants their machine to run without hiccups, recognising the differences between generations ensures compatibility and future-proofing.
For example, the leap from DDR4 to DDR5 RAM introduced a whole new level of speed and bandwidth, making earlier generations feel like dial-up compared to fibre optics. So, understanding how many motherboard generations are there is an essential part of selecting the right platform for your ambitions.
Major Motherboard Generations and Platforms
Intel Motherboard Generations – From early Intel chipsets to latest release
Across the vast landscape of computing, understanding how many motherboard generations are there can feel like unlocking an ancient, ever-evolving treasure chest. Each generation marks a leap forward in technology, shaping the possibilities of what modern systems can achieve. For Intel, these advancements are like chapters in a grand saga, from the humble beginnings of early chipsets to the sophisticated platforms of today. The journey is both fascinating and complex, revealing a tapestry woven with innovation and precision.
Major motherboard generations and platforms for Intel have transformed dramatically over the years. From the first Intel 4004 to the latest 13th Gen Intel processors, each release brings new features, improved connectivity, and enhanced performance. The evolution can be categorised into distinct eras, such as the classic Socket 370 era or the more recent LGA 1700 platform, each with unique architectural standards.
- Introduction of DDR memory standards
- Transition from AGP to PCIe slots
- Advancements in USB and M.2 connectivity
These milestones are pivotal in answering the question of how many motherboard generations are there, offering a clear picture of technological progress.
AMD Motherboard Generations – Evolution of AMD architectures and chipsets
Throughout the evolution of computer technology, one question echoes persistently: how many motherboard generations are there? For AMD, understanding this progression reveals a fascinating story of innovation and resilience. From the early days of the AMD K6 and Athlon processors, each new generation of AMD motherboards has brought significant leaps in performance, efficiency, and connectivity. These advancements are not merely technical milestones but represent the backbone of countless personal and professional pursuits, powering everyday life with silent steadfastness.
AMD motherboard generations have evolved alongside their processors, shaping the landscape of desktop computing. The shift from socket A to AM3+, and then to the modern AM4 and AM5 platforms, reflects a deliberate march of progress. These platforms introduced features like DDR3 and DDR4 memory standards, PCIe 4.0, and enhanced VRM designs—each step a chapter in the ongoing story of technological ingenuity. For those curious about how many motherboard generations are there, understanding this timeline reveals a tapestry woven with innovation and adaptation.
In fact, the journey can be broken down into distinct eras:
- Early socket-based motherboards supporting DDR memory
- Transition to DDR3 with the AM3 platform
- The advent of the AM4 socket, supporting DDR4 and PCIe 4.0
- The latest AMD platforms, like AM5, introducing DDR5 memory and PCIe 5.0
Each generation embodies a new chapter of evolution, reflecting AMD’s commitment to pushing boundaries and empowering users. So, when pondering how many motherboard generations are there, it’s clear that each era stands as a testament to relentless progress—an enduring legacy etched into the very circuitry that fuels our digital lives.
Other Compatible Platforms – Qualcomm, VIA, and emerging technologies
The tapestry of motherboard evolution is a compelling saga, woven through decades of technological innovation. When pondering how many motherboard generations are there, one begins to appreciate the intricate layers of progress, from the earliest days of socket-based architecture to the sophisticated platforms of today. Each generation stands as a sentinel of advancement, guiding us through the shifting landscape of connectivity and performance.
Beyond the dominant players like AMD and Intel, other compatible platforms have contributed their unique threads to this fabric. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chipsets, VIA’s versatile motherboards, and emerging technologies such as ARM-based systems challenge the traditional narrative, expanding the horizons of what a motherboard can be. These innovations signal a future where compatibility and adaptability are paramount.
In truth, the question of how many motherboard generations are there is a journey in itself—an odyssey that spans architecture, standards, and design philosophy. Whether through the lens of classic chipsets or groundbreaking architectures like PCIe 5.0 and DDR5, each era embodies a chapter of relentless pursuit, echoing the unyielding human desire to push boundaries and redefine possibility.
Key Features & Differences Across Generations
Socket Types and Compatibility – Understanding socket changes over generations
Understanding how many motherboard generations are there is like tracing the evolution of a familiar landscape—each new iteration bringing subtle yet significant changes. One key feature that differentiates these generations is the socket type, which acts as the physical and electrical interface between the CPU and the motherboard. As technology advances, socket designs evolve, often requiring users to consider compatibility carefully. For instance, the transition from LGA 1151 to LGA 1200 marked a notable shift in power delivery and pin configuration, making it necessary to upgrade both CPU and motherboard in tandem.
Compatibility becomes a vital concern when assessing different motherboard generations. Motherboard sockets are not always backwards compatible, meaning that a motherboard designed for one generation may not support CPUs from an earlier or later generation without a BIOS update or physical modification. This is why understanding the specific socket type—such as the AM4 for AMD or LGA 1700 for Intel—is crucial for selecting the right motherboard for your needs.
- Socket Type Variations
- Chipset Features and Support
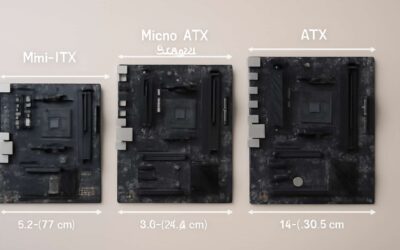
- Physical Dimensions and Layout
- Power Delivery and Overclocking Capabilities
By recognising these distinctions, users can better navigate the complex landscape of motherboard generations, ensuring their systems are both compatible and future-proof. After all, knowing how many motherboard generations are there allows enthusiasts and professionals alike to make informed decisions that stand the test of time in this rapidly evolving digital world.
Chipset Advancements – Technological improvements in chipsets
Motherboard technology has come a long way, and surprisingly, the number of motherboard generations has grown into a fascinating saga of innovation. Each new generation often introduces chipset advancements that push the boundaries of what your PC can do. These technological improvements include faster data transfer rates, enhanced power delivery, and support for cutting-edge peripherals. For example, the jump from Intel’s 8th to 12th generation brought a seismic shift with PCIe 4.0 and DDR5 support, radically transforming performance capabilities.
Understanding how many motherboard generations are there isn’t just a matter of curiosity; it’s a vital piece of the compatibility puzzle. The evolution often features:
- New socket types
- Advanced chipset features
- Improved overclocking potential
- Enhanced I/O options
Recognising these distinctions helps enthusiasts and professionals alike to navigate the ever-changing landscape, ensuring their systems are not only compatible today but also ready for tomorrow’s technological marvels. After all, knowing how many motherboard generations are there is the first step towards building a future-proof rig that stands the test of time!
Memory Support – RAM standards and capacity evolution
As technology continues its relentless march forward, the evolution of motherboard memory support reveals a captivating story of progress. Over successive generations, RAM standards have soared, transforming from modest capacities to colossal amounts that power today’s demanding applications. Each new motherboard generation introduces support for the latest memory standards, such as DDR4 and DDR5, often accompanied by increased maximum capacities, enabling multitasking and high-performance computing with ease.
For example, early generations supported up to 32GB of RAM, but modern boards now easily accommodate 128GB or more, unlocking new horizons for creative professionals and gamers alike. The rapid evolution raises an intriguing question: how many motherboard generations are there? The answer is a tapestry woven with technological milestones, each marking a leap in memory speed, capacity, and efficiency.
- First-generation motherboards supported DDR, the original DDR SDRAM.
- Subsequent generations introduced DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4, each with faster speeds and higher capacities.
- The latest, DDR5, pushes boundaries further, offering even greater bandwidth and future-proofing capabilities.
This constant renewal not only shapes the architecture of modern PCs but also keeps enthusiasts eager to explore the next chapter in motherboard evolution. Truly, understanding how many motherboard generations are there is essential to grasping the full spectrum of memory support and system potential.
Expansion and Peripherals – PCIe versions, USB standards, and other interfaces
The landscape of motherboard technology is a constantly shifting mosaic, with each new generation ushering in a wave of innovative features. One of the most captivating aspects is how expansion and peripherals have evolved—think PCIe versions, USB standards, and other interfaces that define system connectivity. Over successive motherboard generations, these interfaces have undergone remarkable transformations. For instance, PCIe has advanced from version 2.0 to PCIe 5.0, delivering blistering data transfer speeds essential for high-end graphics cards and NVMe SSDs.
Furthermore, USB standards have expanded from USB 2.0 to USB4, offering unprecedented bandwidth and power delivery. This evolution is not merely incremental; it fundamentally reshapes what modern systems can achieve. To grasp the full scope of these advancements, it’s crucial to understand how many motherboard generations are there. This knowledge reveals the technological milestones that separate legacy systems from cutting-edge architectures, shaping the future of PC performance and connectivity.
Categorizing Motherboard Generations
Historical Timeline of Generations – Chronological milestones
The evolution of motherboards is a fascinating journey through technological milestones, each generation marking a leap forward in performance, connectivity, and compatibility. As technology advances at a dizzying pace, understanding how many motherboard generations are there becomes crucial for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Over the decades, these generations have been categorised based on significant breakthroughs, such as new socket types, chipset architectures, and memory standards.
Historically, the timeline of motherboard generations reveals a pattern of rapid innovation. For example, the transition from the first Intel 4004 microprocessor to modern platforms like PCIe 4.0 and DDR5 memory illustrates a continuous march of progress. To better grasp this progression, consider these key milestones:
- Early 1980s: The dawn of personal computing with the first AT motherboards.
- 1990s: Introduction of ISA and PCI slots, expanding expansion options.
- 2000s: The rise of SATA interfaces and AGP to PCI Express transition.
- 2010s: DDR4 memory support, M.2 slots, and USB-C standards emerge.
- 2020s: The latest generations focus on PCIe 5.0, DDR5 RAM, and enhanced power delivery systems.
Each generation, from the pioneering days of the 1980s to the cutting-edge platforms of today, reflects a continuous cycle of innovation. So, how many motherboard generations are there? The answer depends on how these technological milestones are classified, but the timeline underscores a fascinating story of relentless progress and adaptation in the realm of computing hardware.
Current Generations in Market – What is currently available
In the ever-evolving landscape of computing hardware, understanding how many motherboard generations are there can feel like trying to count stars in a vast night sky. The progression is marked not just by incremental improvements but by seismic shifts in technology that redefine what a motherboard can do. Currently, the market showcases several distinct generations, each bringing fresh standards, socket types, and chipset architectures. These generations are categorised based on critical milestones such as support for new memory standards like DDR5, PCIe advancements, and power delivery innovations.
Today’s motherboards span from the foundational early 2000s models supporting DDR2 and PCI Express 2.0 to cutting-edge platforms featuring PCIe 5.0, DDR5 RAM, and ultra-fast NVMe slots. The range is broad, reflecting the rapid pace of technological breakthroughs. To better understand the current landscape, consider these key motherboard generations in the market:
- Intel 12th and 13th Gen (Alder Lake and Raptor Lake) with LGA 1700 sockets
- AMD Ryzen 7000 series with AM5 sockets supporting DDR5
- Earlier Intel 11th Gen boards supporting PCIe 4.0
- Older AMD Ryzen boards supporting PCIe 3.0 and DDR4 standards
As technology continues to accelerate, the number of motherboard generations keeps expanding, each representing a chapter in the story of relentless innovation. Knowing how many motherboard generations are there allows enthusiasts and professionals to navigate this complex terrain with confidence, ensuring compatibility, and future-proofing their investments.
Future Prospects – Emerging technologies and upcoming generations
As technology hurtles forward like a shadowy wraith across the digital night, the question lingers: how many motherboard generations are there? Each new dawn reveals a fresh chapter in the relentless evolution of hardware, haunted by the spectres of innovation. The future promises emerging technologies that will push boundaries even further, blurring the lines between the possible and the impossible.
Upcoming generations are poised to embrace breakthroughs such as PCIe 6.0, enabling data transfer speeds that seem almost supernatural. Additionally, the advent of DDR6 memory and advanced AI-driven chipsets will redefine performance standards. These innovations will inevitably lead to new socket types and architecture standards, creating a labyrinthine landscape for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
To grasp the full scope of this ongoing saga, consider this: the trajectory of motherboard development is not linear but a spiralling ascent into the unknown. Each generation, whether heralding the dawn of quantum computing integration or the resurgence of customisable architecture, adds a new layer to this intricate tapestry. While the precise count of how many motherboard generations are there remains fluid, one thing is certain — the march of progress continues, dark and unyielding, into the shadowed future.
How to Identify Your Motherboard Generation
Checking Motherboard Specifications – Tools and methods
Knowing how many motherboard generations are there can seem as perplexing as deciphering ancient runes—especially with technology advancing faster than a caffeine-fuelled coder. To identify your motherboard’s generation, start by checking its specifications, which are often nestled in the BIOS or system info.
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, tools like CPU-Z or Speccy can reveal vital details about your motherboard’s architecture. Alternatively, inspecting the model number physically on the motherboard can provide clues, especially when cross-referenced with manufacturer datasheets.
If you’re feeling particularly adventurous, a quick search online using your motherboard’s exact model will often tell you the generation at a glance. Remember, understanding how many motherboard generations are there isn’t just a matter of curiosity—it’s essential for ensuring compatibility with the latest CPUs, RAM standards, and expansion interfaces.
Physical Inspection – Locating model numbers and codes
Unearthing the secrets of your motherboard’s lineage can feel like deciphering an ancient code—mysterious but immensely rewarding. When it comes to understanding how many motherboard generations are there, physical inspection plays a pivotal role. The model number, often etched into the motherboard’s surface, is your first clue in this digital detective game. Carefully locate this alphanumeric code, typically near the CPU socket, RAM slots, or along the edges. Once identified, cross-referencing this number with manufacturer datasheets or online repositories can reveal the exact generation.
To simplify the process, consider these steps:
- Power down your system and unplug it for safety.
- Remove the side panel to access the motherboard.
- Locate the model number, often printed directly on the PCB or on a sticker.
- Note down this identifier and perform an online search or consult the manufacturer’s website.
This physical inspection method is often the fastest way to determine how many motherboard generations are there, especially when combined with visual cues like socket type and chipset markings. Such details unlock the evolutionary story of your motherboard, revealing whether it aligns with the latest standards or belongs to a bygone era—an essential step for compatibility and system upgrades. The intrigue lies in the subtle variations, making each motherboard a chapter in the ongoing saga of technological advancement.
BIOS/UEFI Identification – Accessing firmware information
Accessing the BIOS or UEFI firmware provides a straightforward way to determine how many motherboard generations are there in your system. When you boot up your computer, pressing a specific key—often F2, DEL, or ESC—grants entry to the firmware interface. Within this environment, look for system information or version details, which often include the motherboard’s chipset or model name. This data can reveal the exact generation of your motherboard, especially when cross-referenced with manufacturer documentation.
To streamline the process, consider this quick check:
- Power on your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI setup.
- Navigate to the ‘System Information’ or ‘Main’ tab.
- Note the motherboard model or chipset details.
- Use this information to identify the motherboard’s generation through online resources or manufacturer websites.
This method is invaluable because it provides real-time, precise data directly from your motherboard’s core firmware. By understanding your motherboard’s generation, you can better gauge compatibility for upgrades and future-proofing, answering the question of how many motherboard generations are there with clarity and confidence!
FAQs about Motherboard Generations
Are Motherboard Generations Compatible with All CPUs? – Compatibility considerations
When delving into the labyrinthine world of motherboards, one question echoes with curiosity: how many motherboard generations are there? The answer isn’t static; it’s a dynamic tapestry woven from technological leaps, industry standards, and evolving architectures. Each generation signifies a milestone, a leap forward in performance, connectivity, and efficiency. But a common misconception persists—are motherboard generations compatible with all CPUs? Not quite. Compatibility hinges on specific socket types, chipset standards, and firmware support. Modern motherboard generations often introduce new socket designs, making them incompatible with earlier CPUs without adapters or modifications. Therefore, knowing the exact generation, and how it aligns with your processor, becomes crucial. This knowledge ensures seamless upgrades and avoids costly mismatches, transforming your PC build into a harmonious symphony of hardware and software compatibility!
Can I Upgrade My Motherboard to a Newer Generation? – Upgrade feasibility and limitations
Upgrading your motherboard isn’t always straightforward. Many wonder, “Can I upgrade my motherboard to a newer generation?” The answer depends on several factors. While technology advances rapidly, compatibility issues often limit direct upgrades. Motherboard generations differ significantly in socket design, chipset, and firmware support. In most cases, a motherboard upgrade means replacing the entire unit. However, understanding how many motherboard generations are there helps clarify your options. For instance, each new generation typically introduces improved memory support, faster PCIe standards, and enhanced connectivity. But keep in mind, compatibility with your existing CPU or components isn’t guaranteed. Sometimes, a new motherboard may require a different processor or RAM standard, which could lead to additional upgrades. Ultimately, the feasibility of upgrading hinges on your specific hardware and what features you need. So, if you’re eyeing the latest tech, be prepared for a full motherboard swap—knowing how many motherboard generations are there simplifies this decision significantly.
Why Do Motherboard Generations Matter? – Impact on performance and future-proofing
Motherboard generations are the silent architects of our digital worlds, shaping the very fabric of performance and compatibility. As technology accelerates at a breakneck pace, understanding how many motherboard generations are there becomes a vital quest for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Each new generation often heralds a leap forward—faster PCIe standards, improved memory support, and cutting-edge connectivity—yet, these advancements can also bring compatibility conundrums.
Knowing how many motherboard generations are there isn’t just a matter of curiosity; it’s a portal to future-proofing and making informed upgrades. From the early days of Intel’s pioneering chipsets to AMD’s revolutionary architecture shifts, each generation weaves its own story. Whether you’re contemplating a hardware refresh or exploring emerging technologies, grasping the timeline and evolution of motherboard generations reveals the intricate dance of innovation, guiding your decisions with clarity and confidence.

0 Comments